By Joe Navarro
This post summarize the book What Every BODY is Saying by Joe Navarro.
Part 1
Eye blocking
Like you: raise or arch their eyebrows
Doesnʼt like you: squint their eyes slightly
Same thing when you lie or not at your ease.
Under panic
Under panic or under shock, your “thinking” brain deactivate and you can do stupid things.
Lips pressure
Troubled and/or something is going wrong.
There are universal body languages and some specific to each person. The more you know someone the more you can interpret them.
Be attentive to changes in behaviors.
Most important is to distinguish between comfort and discomfort behaviors.
Part 2 – 3Fs
We have 3 brains: reptilian (stem), mammalian (limbic) and human (neocortex). Nonverbal is commanded by limbic one.
Freeze: Turtle effect when you donʼt want to be seen, or lose confidence (thief, abused child…).
Flight (uncomfortable) – Blocking behaviors: closing eyes, rubbing the eyes or placing the hands in front of the face. Distance herself from someone, lean away, placing objects in between, bag on her lap, or turning her feet toward the nearest exit.
Fight: Eye blocking is a very powerful display of consternation, disbelief, disagreement. Arguments is a form of fighting reaction.
Pacifying behaviors
Whenever there is a limbic response, especially negative, it will be followed by pacifying behaviors.
- Touch or stroke the neck (or suprasternal natch for women) or mouth is a pacifying behavior that can show uncomfort, stress, insecure.
- Touch/play with our hair,
- rubbing our cheeks or our lips from inside with our tongues,
- exhale slowly,
- playing with a necklace or jewelry,
- rubbing of the forehead,
- cheek or face touching,
- any touching of the face, head, shoulder, arm, hand or leg,
- excessive yawning,
- leg cleaner under the table,
- ventilating,
- self body-hug.
Part 3 – Feet
Most honest part of our body are our feet.
Happy feet sign of happiness, excitement. Notice the sudden change to interpret. If for example happy feet then stop…
- Feet direction to know if someone want to stay or leave or even welcome you when you go say hi to a group of people.
- Hands on knees and shifting weight on the feet: time to leave
- Foot toes point upward (gravity-defying behaviors): happy
- Foot in starterʼs position: want to go
- Splayed posture, territory control, defense/attacking mode
- Cross-legs: confortable with someone, suddenly uncross if a threat come
- We Cross-legs toward the most favorite person
- Courtship: shoe playing and mirroring with the partner. Feet proximity/ touching under the table when close to someone. If they touch accidentally and people are not close they will move away.
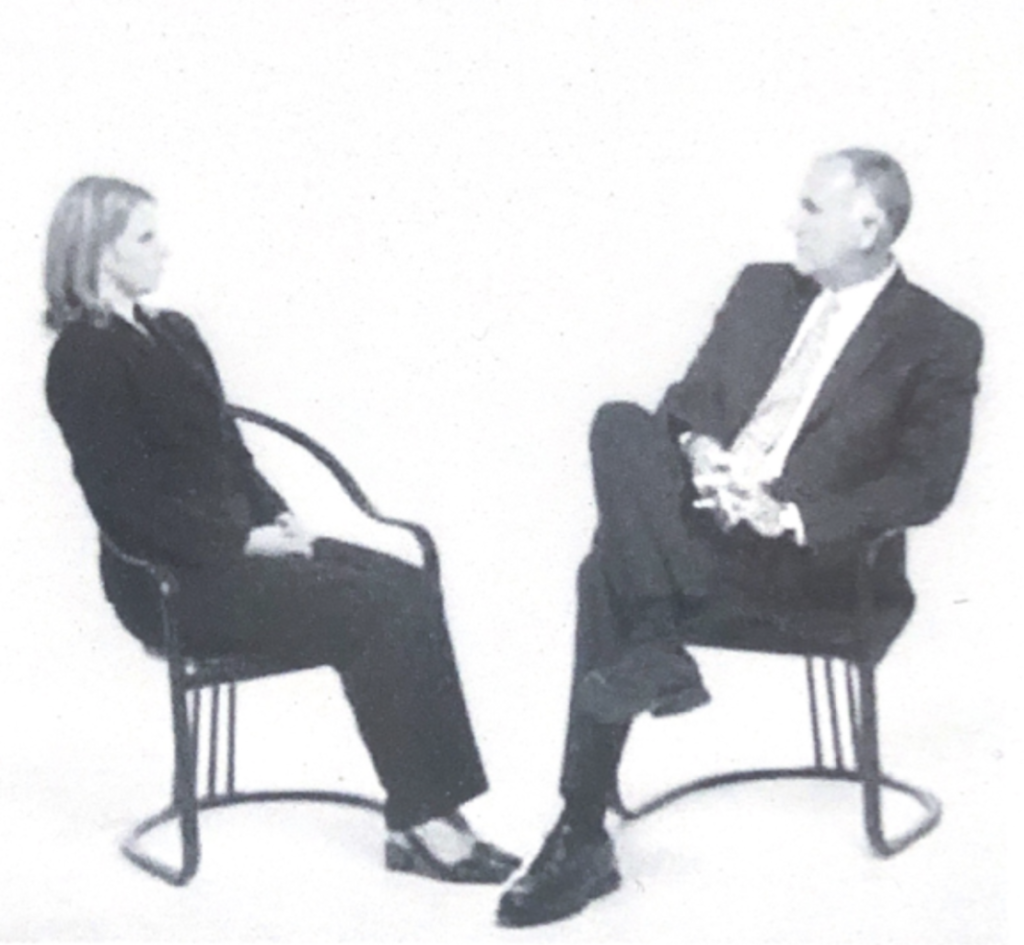


Test first impression / what people feel about you
Hearty handshake, then step back.
- 1- stay where he is: comfortable at this distance
- 2- step back: uncomfortable / want to go away
- 3- step closer: comfortable with you
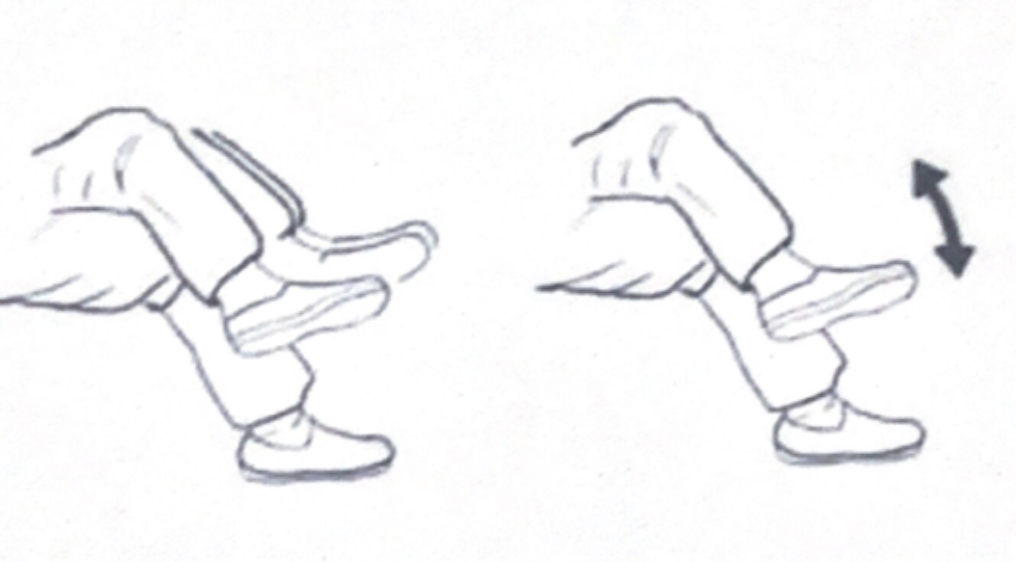
- Foot freeze after moving: discomfort
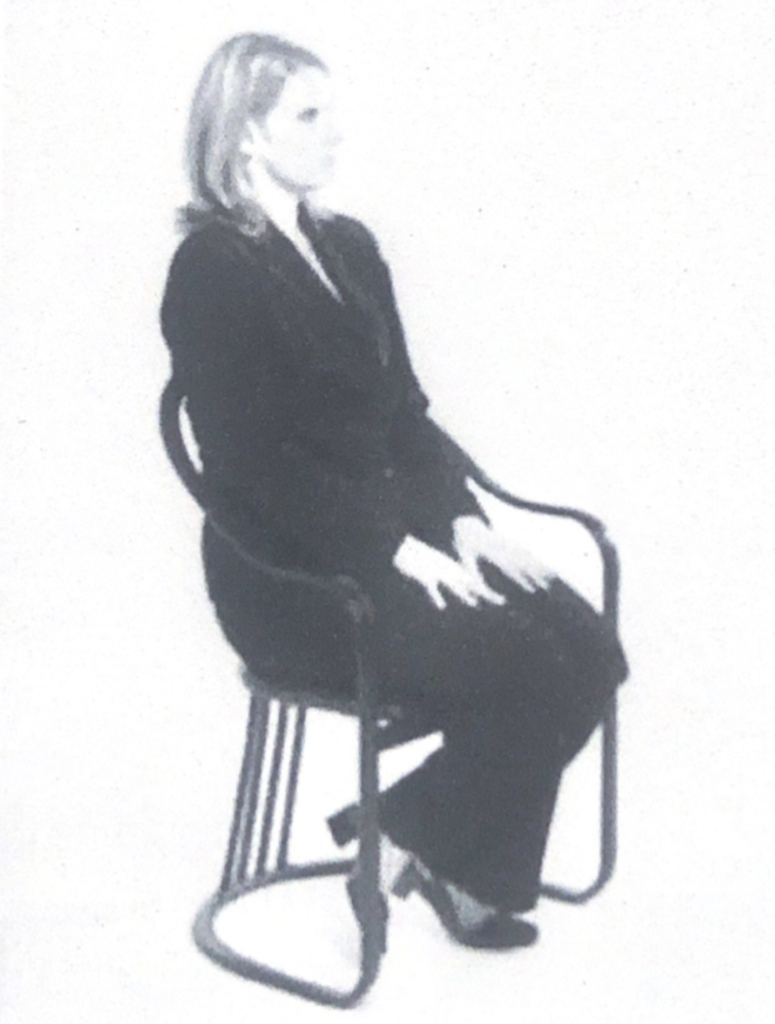

Part 4 – Torso
Ventral leaning toward someone: appreciate, comfort. Lean toward someone to show him you agree with him.
Ventral leaning away (and arm crossing to protect or torso): discomfort
Discomfort/disagreement: cross arms (more grabbed the hand the more discomfort), put an object in between (pillow), button the jacket.
People feel cold when uncomfortable because the blood go mainly in the muscles.
When stressed the blood goes to the muscles, especially the legs, our digestive system stop working, thatʼs why when too much stressed we can vomit.
When sick our brain doesnʼt care anymore about apparence.
Splaying out is a territorial display.
Puffing up the chest before a fight.
When you donʼt know: partial shoulder shrugs indicate lack of commitment, or insecurity (dubious). Instead when both shoulders to rise is sincere.
Shoulders rising toward ears causes the turtle effect, weakness, insecurity, and negative emotions are the message.
Part five – Arms
Happy: arms up.
Freeze: restricted movements of the arms, want to be unnoticed (thiefʼs for example).
“Regal stance”: arms behind the back mean “donʼt dew near”. To keep people at distance.
Arms (territory) spread could indicate high status. In opposite elbows again his waist and arms draped between his legs send a message of weakness and low confidence.
Arms akimbo is a powerful territorial display that can be used to establish dominance or to communicate that there are issues. When thumbs forward: inquisitive. Thumbs are back: authoritative (or there are issues).
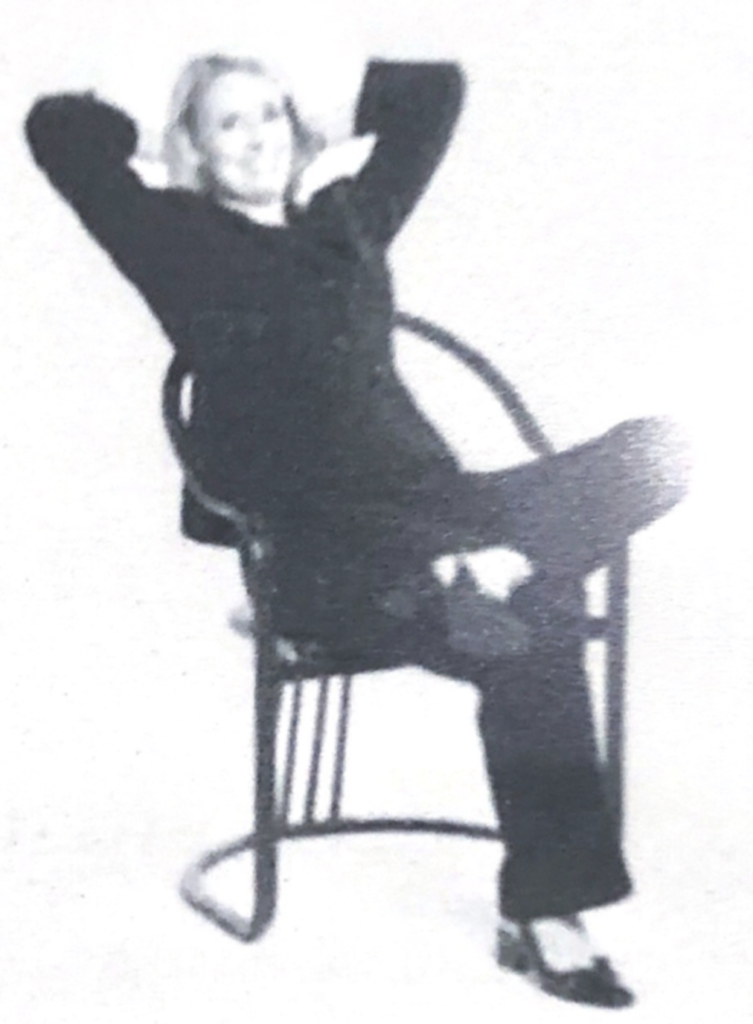
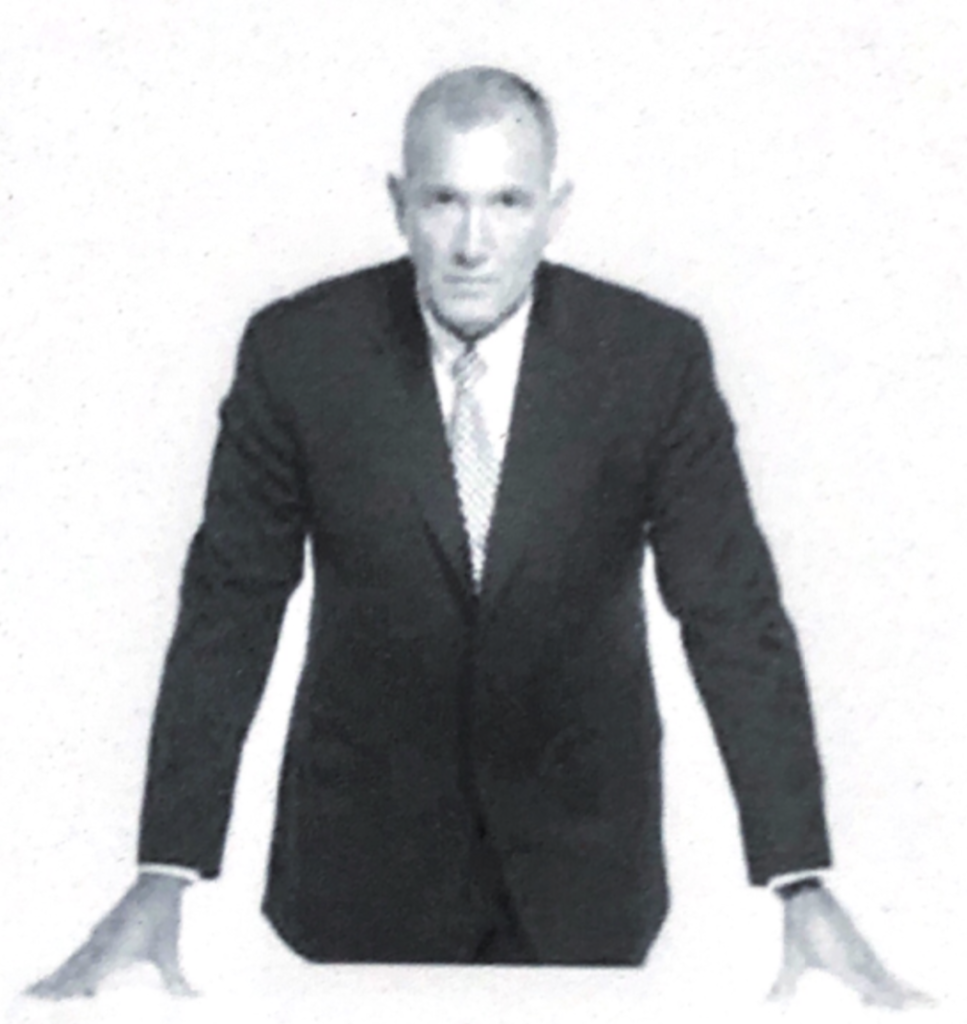
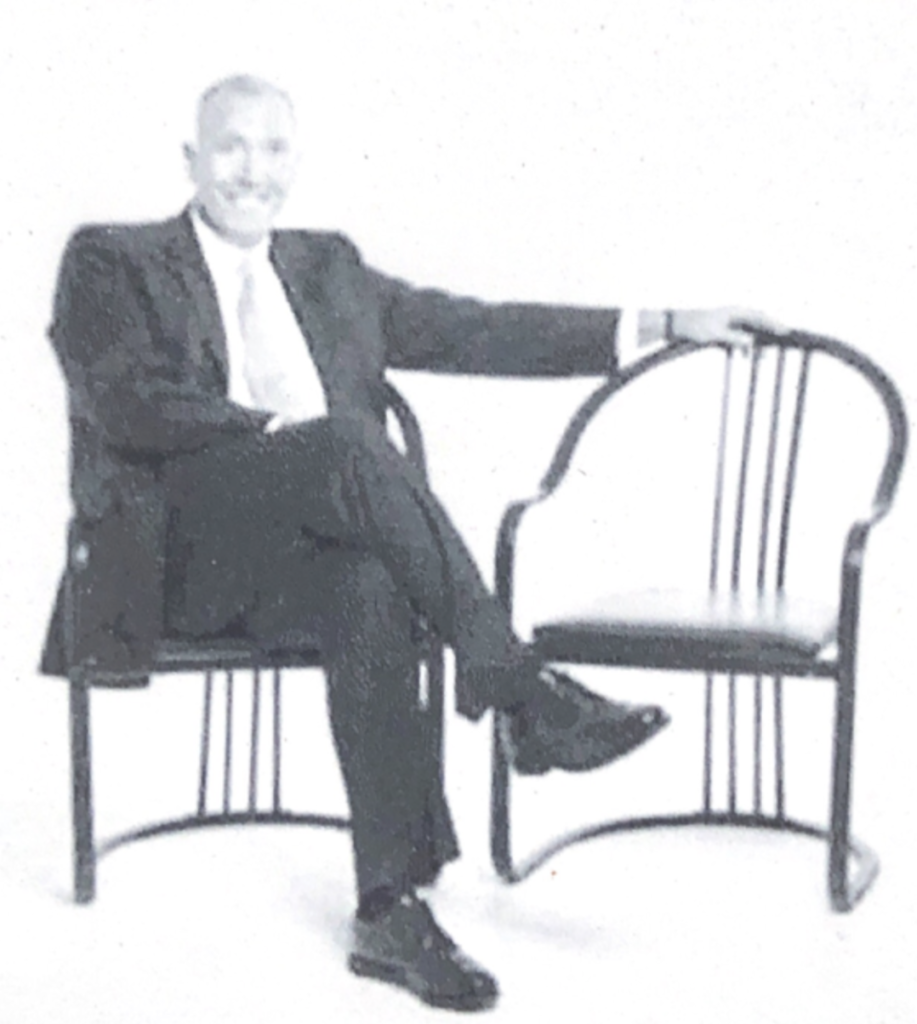



When we place our arms near someone elseʼs, the limbic brain is demonstrating overtly that we are so comfortable, physical contact is permissible.
When we are confident we spread out, when we are less confident we withdraw.
One of the best ways to establish rapport with someone is to touch that person on the arms, somewhere between the elbow and the shoulder.
Part six – Hands and fingers
People may regard you with suspicion if they canʼt see your hands while you are taking.
In any relationship, when there is trust there is more tactile activity.
Pointing is just plain offensive.
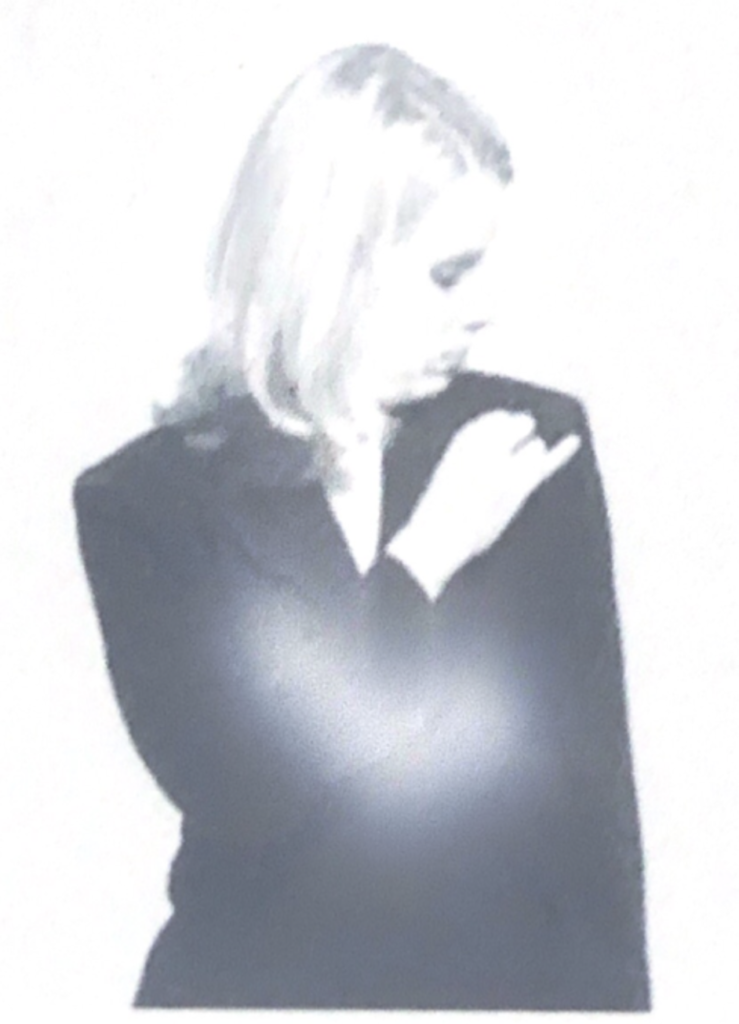

As a general guideline, any shaking behavior would that starts or stop suddenly, or is somehow markedly different from baseline behavior, deserves further scrutiny.
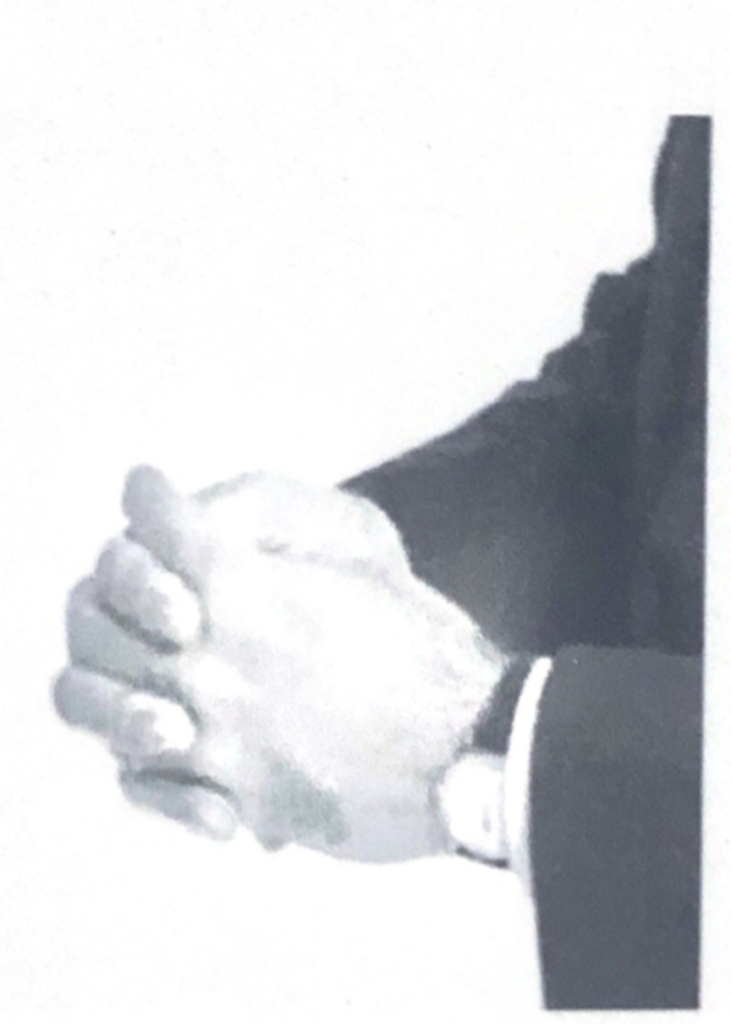
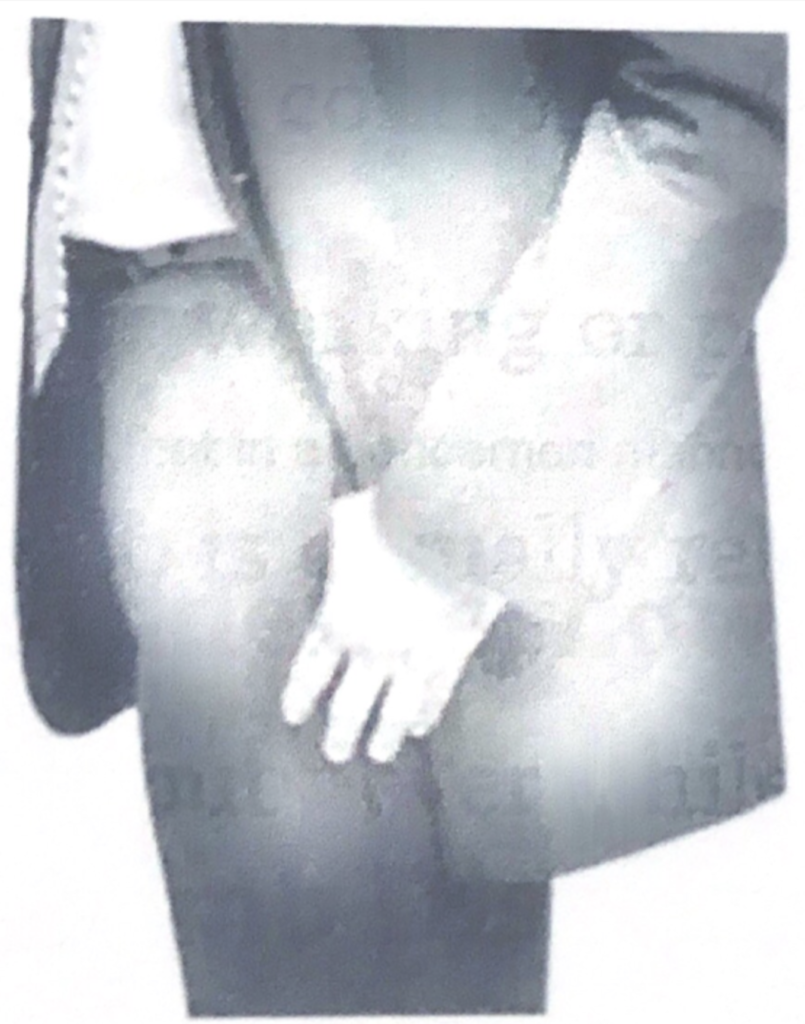
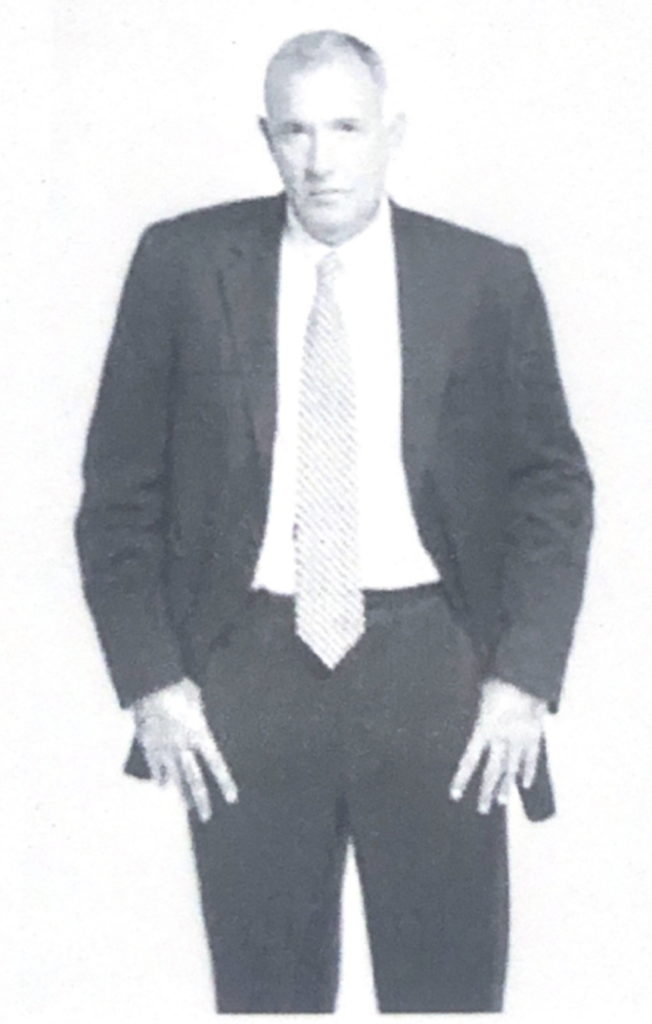
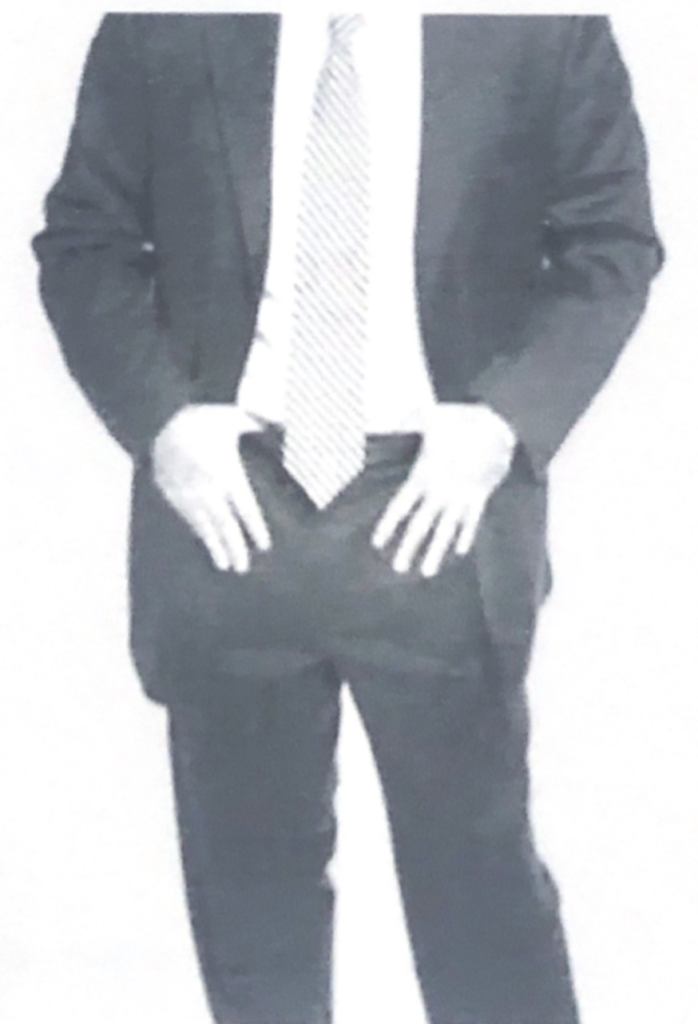








Look for hand and arm movements that are suddenly restrained, they say a lot about what is going on in that person brain.
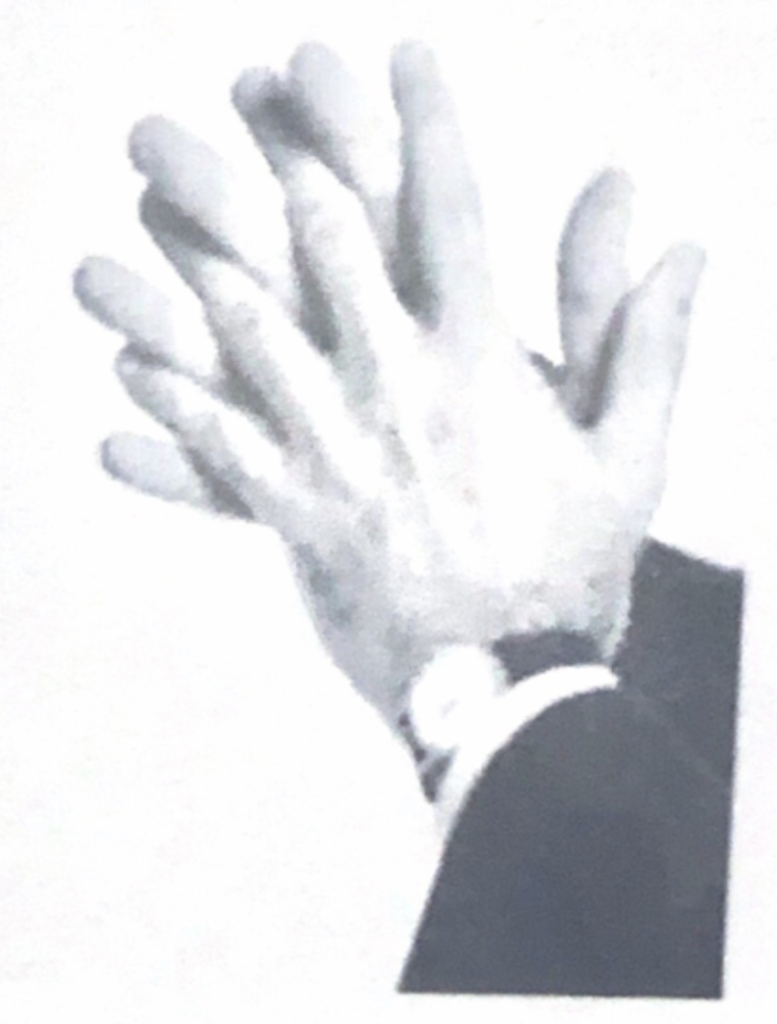
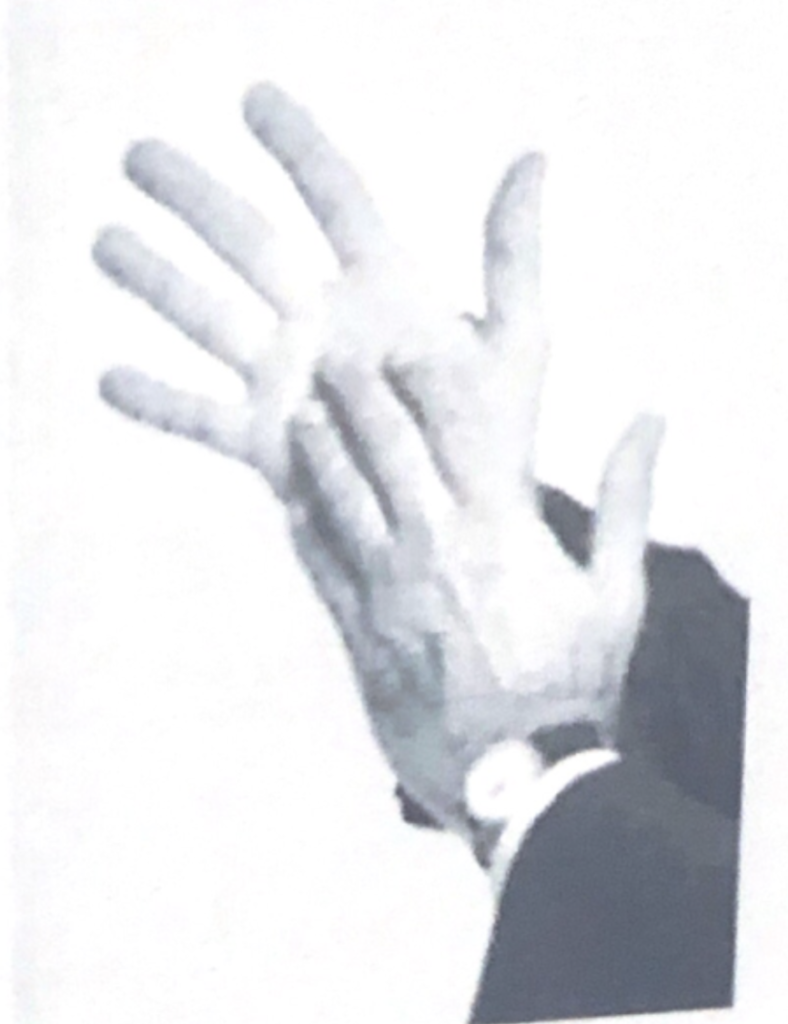

High reliable: People who touch their neck (anywhere) while speaking are reflecting lower than normal confidence or are relieving stress.
Micro expressions of hands: The more reflexive and short lived the behavior is, the more truthful it tends to be.
Hands gradually disappear from the tabletop: low confidence, stress.
Bird finger can move, used to move up glasses when antipathy go around.
Part seven – Face
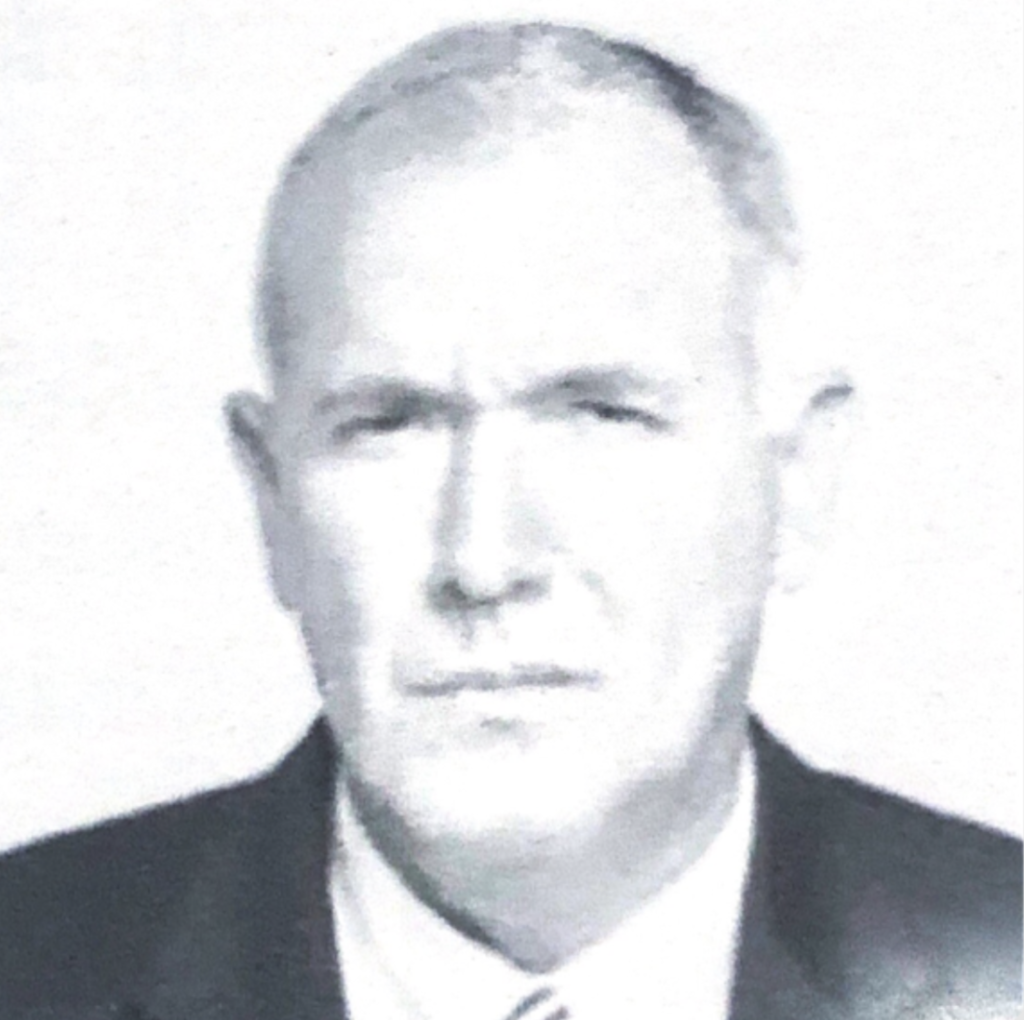

When we are truly relaxed and comfortable, facial muscles relax and the head will tilt to the side, espousing our most vulnerable area, the neck! (High comfort display).

Blocking and openness body languages
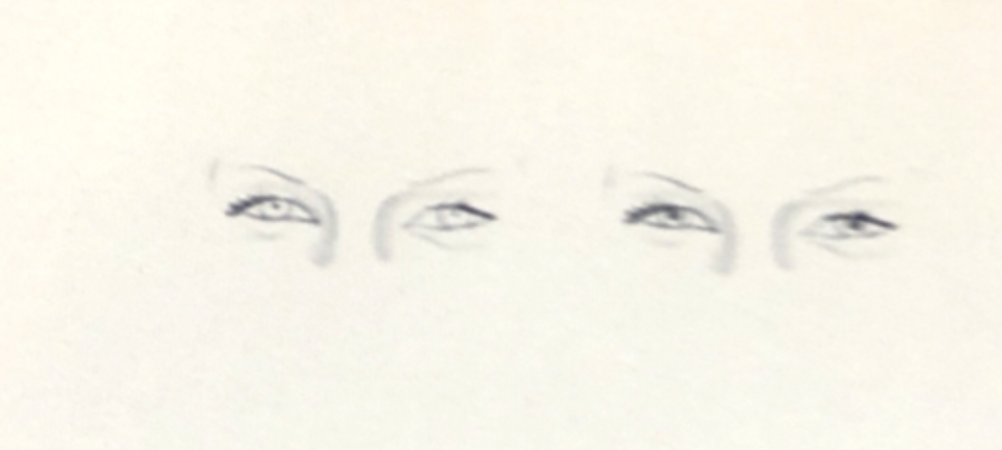

When we become aroused, are surprised, or are suddenly confronted, our eyes open up. To let maximum amount of information go to the brain. If it is perceived negatively, in a fraction of second the pupils will constrict.
Blocking
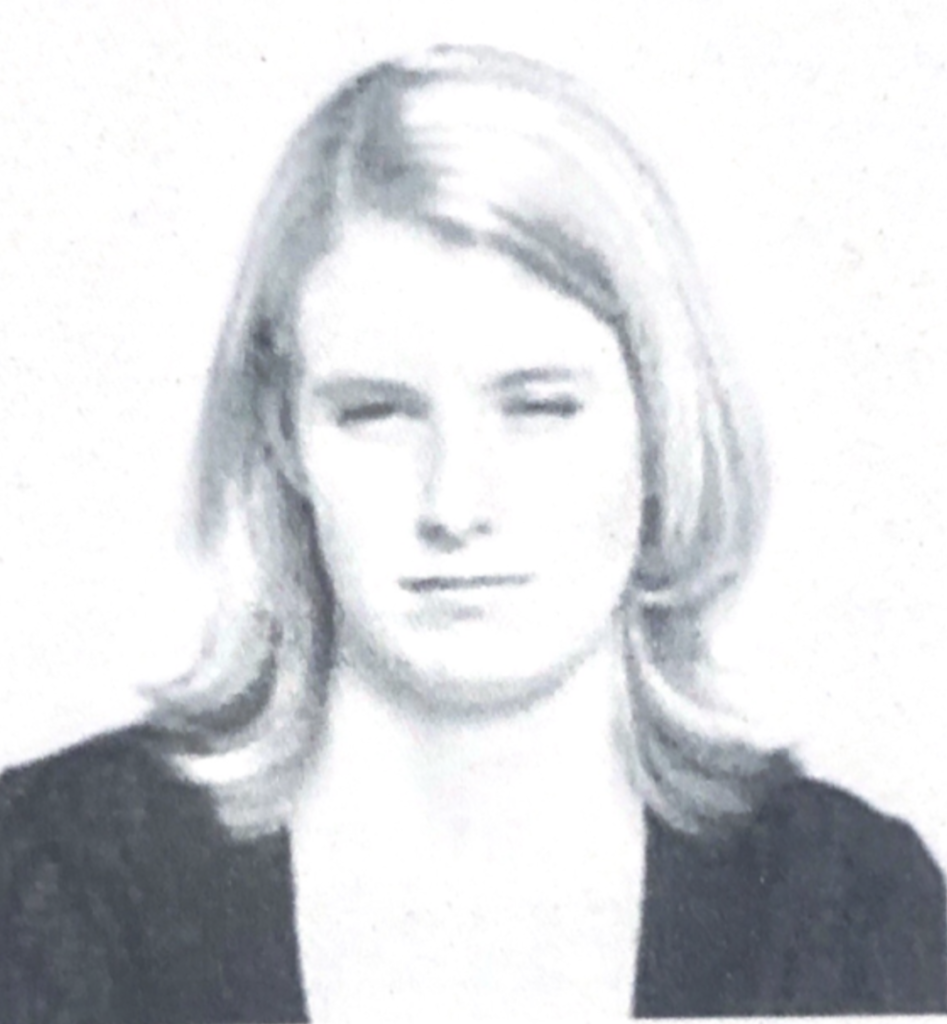
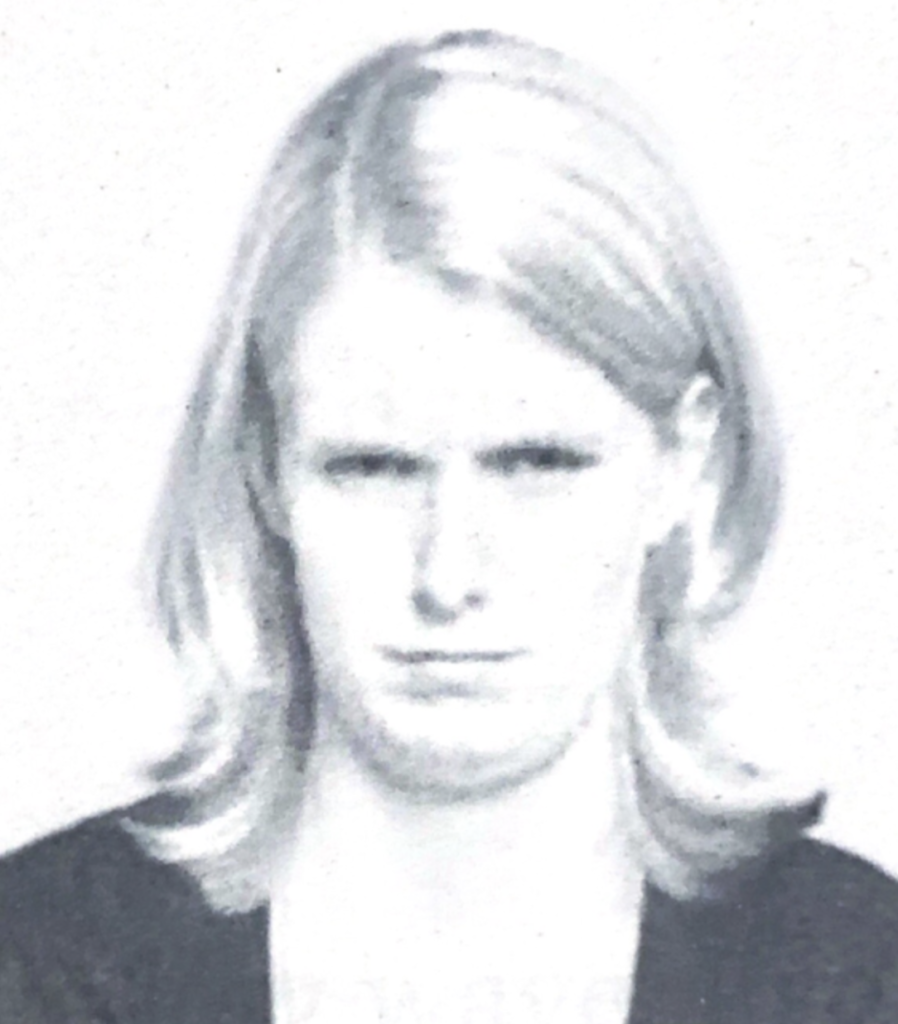


Arched eyebrows signify high confidence and positive feelings (gravity-defying behavior), whereas lowered eyebrows are usually a sign of low confidence and negative feelings, a behavior that indicates weakness and insecurity in a person.
All blocking behaviors are indicative of concern, dislike, disagreement or the perception of a potential threat.
Ex: eyelids close for moments when you hear a bad news.
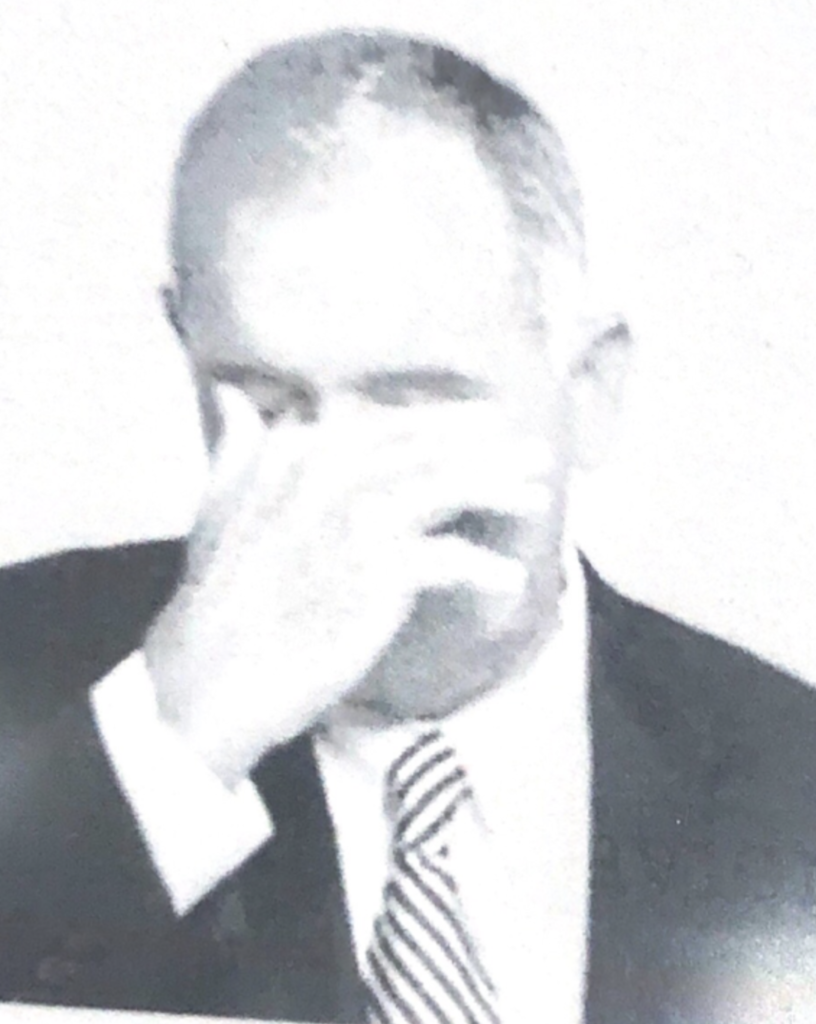
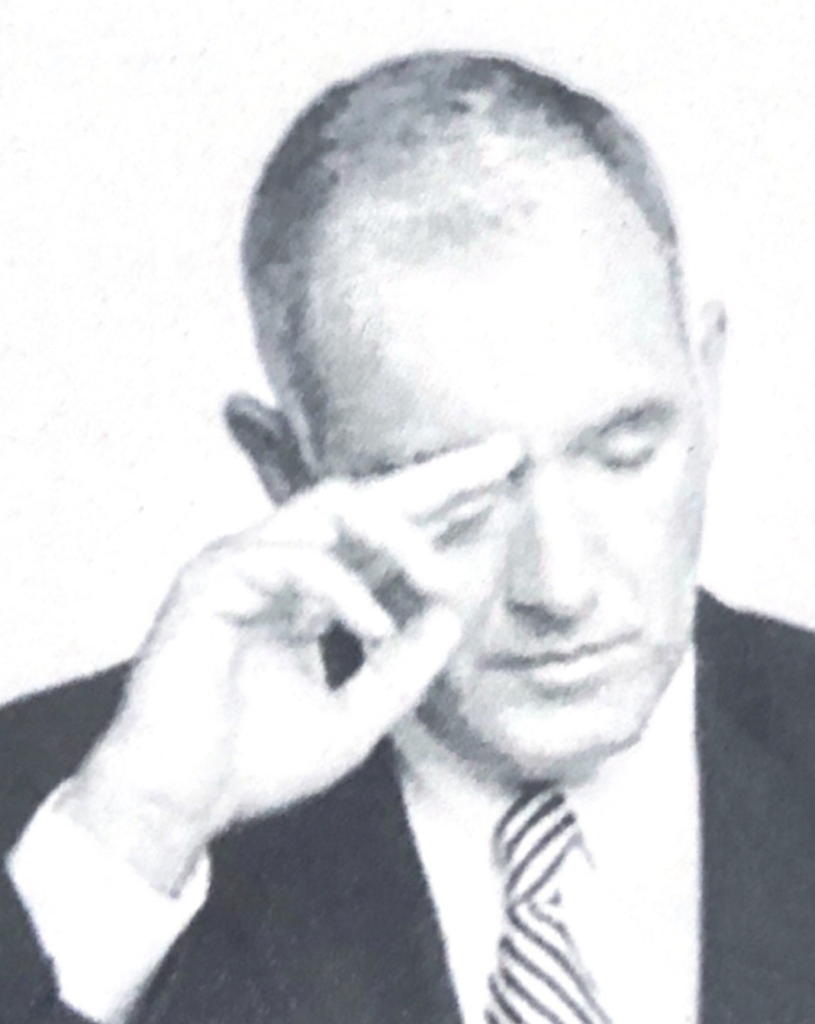




Openess

Arched eyebrows and flashbulb eyes, defying gravity, are a sure sign of positive feelings.
Watch the eyes – the bigger they get, the better things are! On the other hand, when you start to see eye shrinkage, such as squinting, eyebrows dropping, or pupils constricting, you may want to rethink and change your behavioral tactics.
Eye gaze
Do not assume someone is deceptive or disinterested because he looks away. Clarity of thoughts is often enhanced by looking away.
Eye blink
Our blink rate increases when we are aroused, troubled, nervous or concerned, and it returns to normal when we are relaxed.

Mouth





The sneer

Tongue



Nose flaring
Preparing one of three things: argue, run or fight.
Nail Biting
I am insecure.
Blush
When they are caught doing something they know is wrong.
Blanching
Takes place as the involuntary nervous system hijacks all the surface vessels and channels the blood to our larger muscles to prepare for escape or attack.

Gravity defying of the face
What is true for the chin is also true for the nose. A nose gravity defying gesture is a high confidence nonverbal tell, while a nose down position is a display of low confidence.


The negative sentiment will almost always be the more accurate and genuine of the personʼs feelings and emotions.
So when confronted with both, go with the first emotion observed, especially if it is a negative emotion.
If you are confused as to the meaning of a facial expression, reenact it and sense.
Part 8: detecting deception
Those who are lying or are guilty and must carry the knowledge of their lies and/ or crimes with them find it difficult to achieve comfort, and their tension and distress may be readily observed.
Your goal is to establish high comfort during the early part of any interaction or during “report building”. And then detect discomfort when something specific is said.
Try to remain calm as you ask questions, donʼt act suspicious, and appear comfortable and nonjudgmental.
Comfortable with another person
People who are comfortable with each other will move objects aside so that nothing blocks their view. Over time, they may draw closer so they do not have to talk loudly. Individuals who are comfortable display their bodies more openly, showing more of their torsos and insides of their arms and legs. They allow ventral access or fronting.
The tone of each party should mirror the other over time if there is synchrony.
Asynchrony is a barrier to effective communication and is a serious obstacle to a successful interview or discussion.
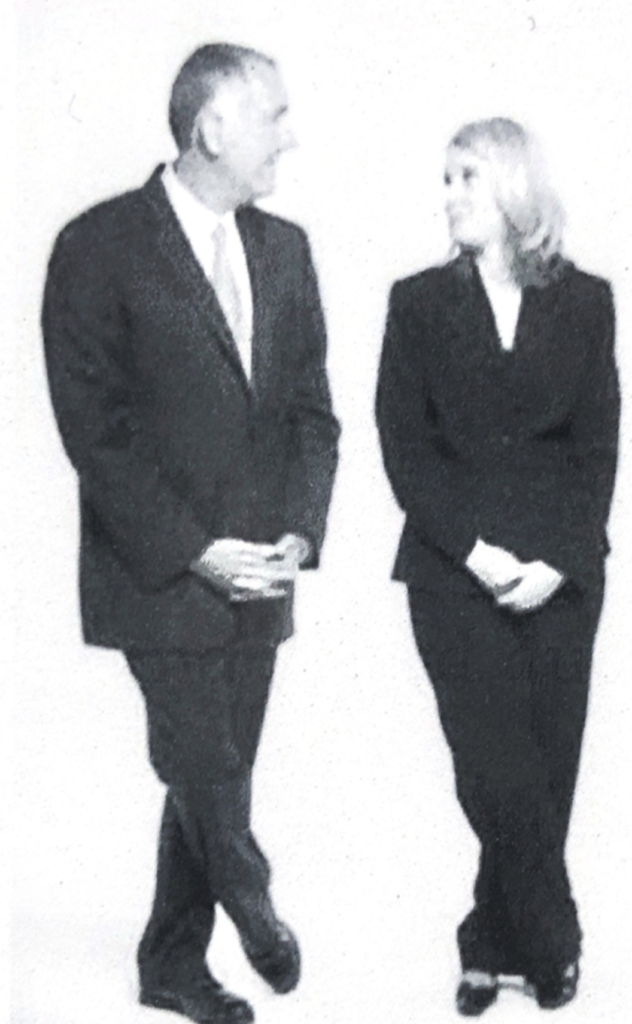

Discomfort with another person
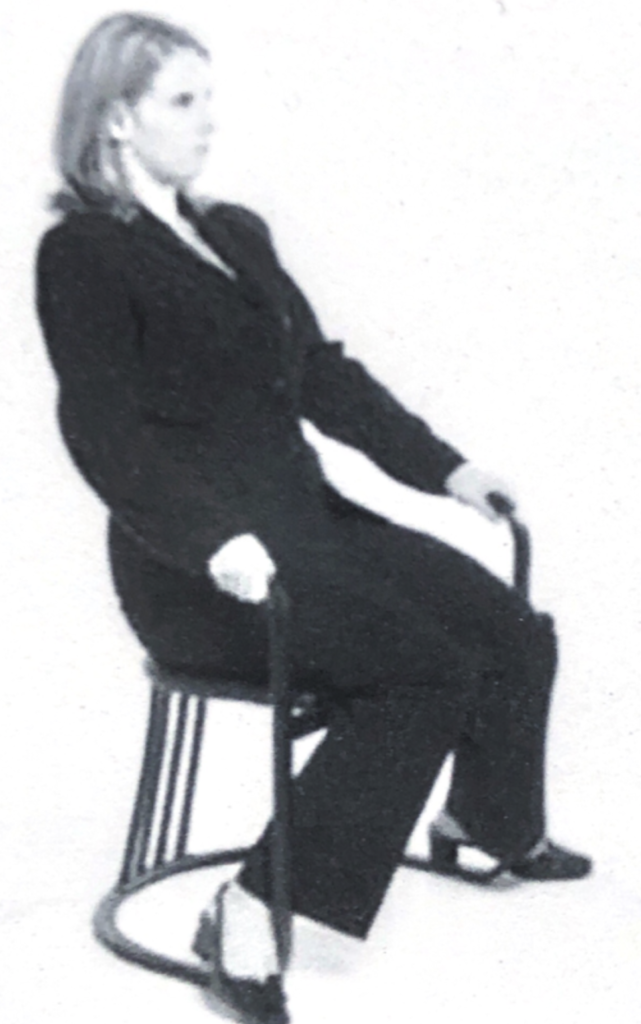
Watch for liars to use obstacles or objects (such as a pillow, drinking glass, or a chair) to form a barrier between you and them.
Even while sitting side by side, we will lean away from those with whom we feel uncomfortable, often moving either our torsos or our feet away or toward an exit.
When making false statements, liars will rarely touch or engage in other physical contact with you. Since touching is more often performed by the truthful person for emphasis, this distancing helps to alleviate the level of anxiety a dishonest person is feeling.
If possible and appropriate, you may consider sitting close to a loved one when questioning him or her about something serious, or even holding your childʼs hand while you discuss a difficult matter. Any diminution of touching is a sign of deception.
We donʼt touch those we donʼt respect or for whom we have contempt.
Interview step by step
- Get a clear view (open space)
- expect some pacifying behaviors
- expect initial nervousness
- get the person with who you are interacting to relax first
- establish a baseline
- look for increased use of pacifiers
- ask, pause, and observe
- keep the person you are interviewing focused
- chatter is not truth
- stress coming in and going out
- isolate the cause of the stress
- pacifiers say so much: not necessarily deception signs but need to further focus on and exploration
Two principal nonverbal behavioral patterns to consider in detecting deception
Synchrony: person answering in the affirmative should have congruent head movement that immediately support what it is said; it should not be delayed. Emphasis: liars do not emphasize (another manifestation of emphasis is seen when someone lean forward with the torso, showing interest). When seated, people emphasize by raising the knee (staccato-like) while highlighting important points, and added emphasis can be shown by slapping the knee as it comes up, indicating emotional exuberance. Gravity defying gestures are emblematic of emphasis and true sentiment, something liars rarely display.
In contrast, people de- emphasize or show lack of commitment to their own speech by speaking behind their hands (talking while covering their mouths) or showing limited facial expression.
Deceptive people spend time evaluating what they say and how it is being received, which is inconsistent with honest behavior.
Lack of emphasis in hand behavior (lack of arm movement for example) is a sign of possible deception.
As individuals make déclarative statement that are false, they will avoid touching not only other people, but objects such as a podium or table as well.
People who are being deceptive lack commitment and confidence in what they are saying. Although their thinking brain (neocortex) will decide what to say in order to mislead, their emotive brain (the limbic system – the honest part of the brain) simply will not be committed to the rude, and therefore will not emphasize their statement using nonverbal behaviors (such as gestures).
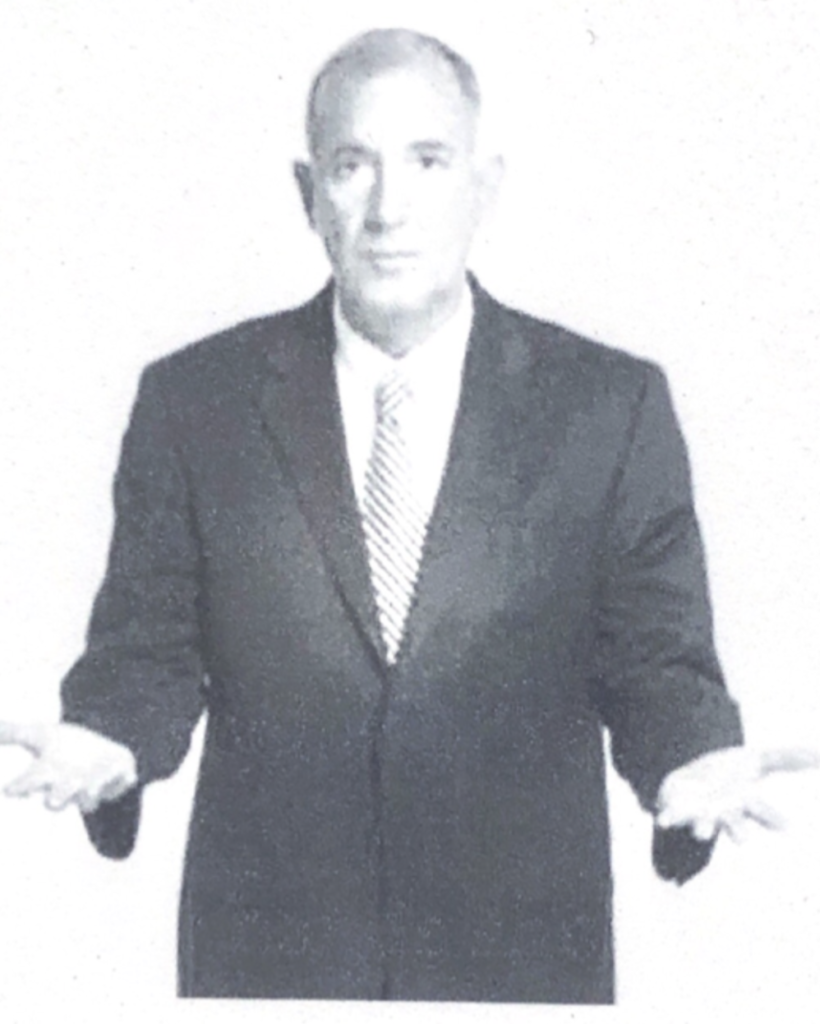
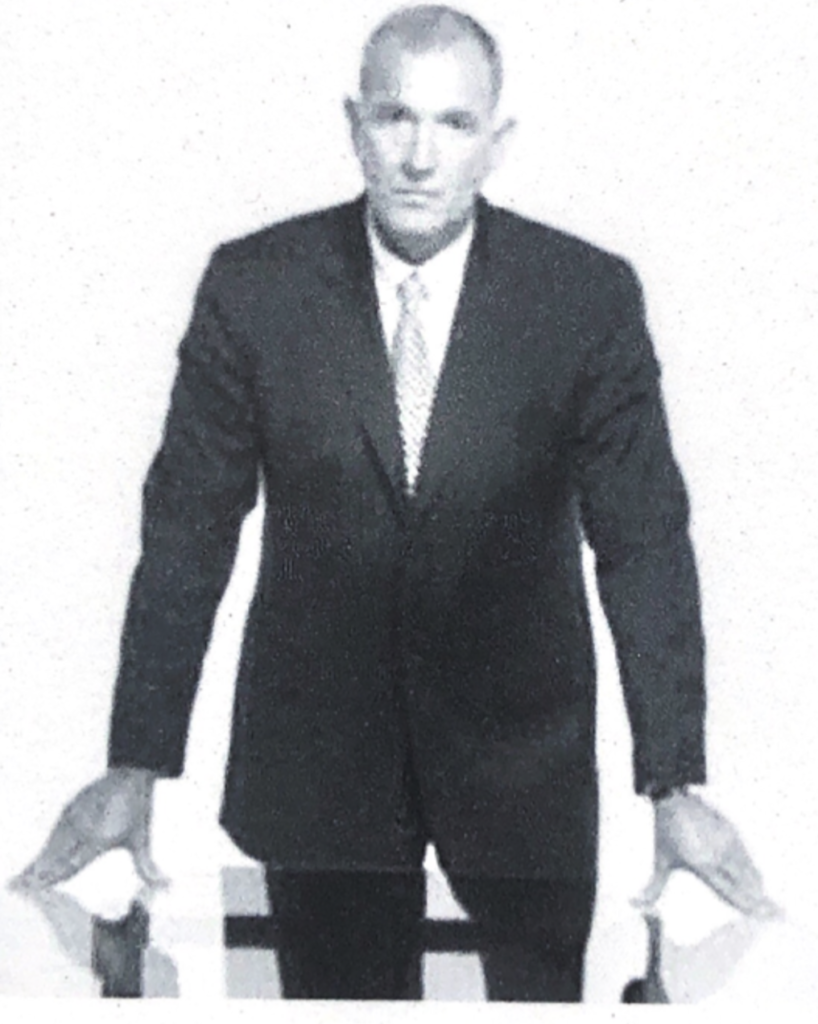



Territorial displays and deception
Those who are insecure, or unsure of themselves, their thoughts will have a turtle effect and try to hide or be little (only one shoulder comes up, or the shoulders rose nearly to the ears, head seems to disappear is a sign of high discomfort and possible deception).
Concluding
A person who is not comfortable, not emphasizing, and whose communication is out of synchrony is, at best, communicating poorly or, at worst, being deceptive.
Part nine: final thoughts
Look for the signs…
