By Erich R. Bühler.
You can find the full size MindMap here.
1- From zero to a million in 2 seconds
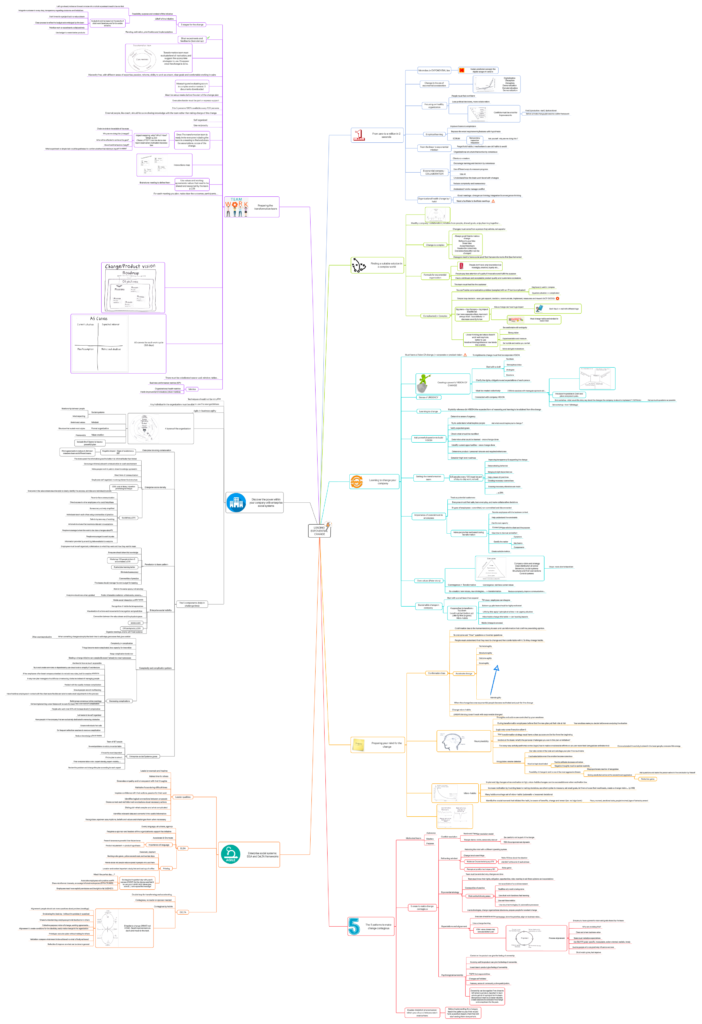
A- Moore law ≠ EXPONENTIAL law

Kodak predicted wrongly the digital usage of cameras. They planned the massive usage of the digital cameras based on the Moore law which was wrong. The usage of digital cameras followed the exponential law.
B- Change in the era of exponential acceleration
The exponential growth steps:
- Digitalization
- Deception
- Disruption
- Demonetization
- Dematerialization
- Democratization
C- Focusing on a healthy organization
- People must feel confident
- Less political decisions, more collaboration in teams and between them
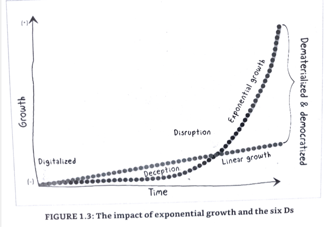
Conflicts must be a tool for improvements
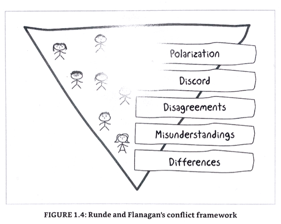
- First 3 productive – last 2 are dysfunctional
- Before activating change plan resolve conflict framework
D- Empirical learning
- Improve thanks to empiricism
- Replace the word requirements/features with
hypothesis in order to be aware that it can be changed in the future.
SCRUM
- Transparency
- Inspection
- Adaptation
Ask yourself : why are we doing this?
E- From the linear to an exponential mindset
Forget hold habits / mechanism to use old habits to avoid
F- Exponential company – COLLABORATION
Organizational structure thatevolve by consensus- Clients co-creators
- Encourage learning and decision by consensus
- Use AI
- Use different ways to measure progress
- Reduce complexity and bureaucracy
- Understand how the brain work faced with changes
- Understand how to manage conflict
G- Organizational health change by 1 habit
- Good meetings: divergence thinking, integration & convergence thinking.
- Need a facilitator to facilitate meetings
2- Finding a suitable solution in a complex world
Healthy company : collaboration, initiative from people, shared goals, enjoy learning together…
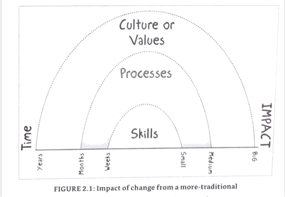
A- Change is complex
Changes must come from a person they admire, not a superior.
- Always good time to make a change
- Believe in your idea
- Share idea
- Accept feedback
- Passion for collectivity
- Decisions from other can be changed
Managers want to have social proof that frameworks works first (which is a bad behavior).
B- Formula for an exponential organization

People don’t look only innovation but nostalgia, emotion, loyalty etc…
- People pay less attention to quality if innovative and fulfill the purpose.
- Have a minimum and acceptable product quality and customers cocreators.
- The team must feel like the customer.
C- Complicated ≠ Complex
You can’t solve a communication problem (complex) with an IT tool (complicated):
- Equation solvation: complicated
- Nephews to watch: complex
Simple loop decision: exec get support, decision, communicate, implement, measures and reward (NOT GOOD).
Big plans = big changes = big impact (traditional thinking). Can have an opposite effect. And don’t always work: fewer defects -> decrease severity to low.
Minus change can have huge impact.

Bank fraud -> mail with different logo
Must change habits and mindset to make it last.
Linear thinking and steps don’t work well anymore. Better to use Iterative thinking (discover new lands like a
- Be comfortable with ambiguity
- Strong vision
- Experimentation and measure
- Be humble and realize you can fail
- Move and gain momentum
3- Learning to change your company

Must have a Vision Of change ≠ corporate or product vision.
To implement a change you must first be corporate VISION.
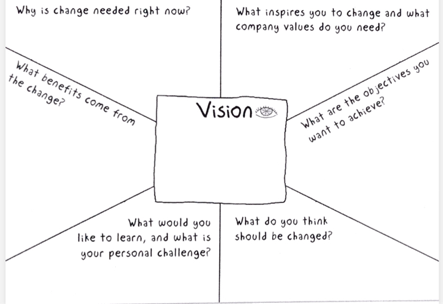
A- Creating a powerful VISION OF CHANGE
Start with a draft:
- Numbers
- Stories/Anecdotes
- Analogies
- Emotions
Clarify the rights, obligations and expectations of each person.
Must be created collectively:
- 2 x 90min sessions with managers sponsors etc…
- Introduce the problem in 2 min and place everyone in pairs.
- 2nd workshop: what would the story say about the changes the company is about to
implement ? (10/15min) - Ask as much questions as possible
- 3rd workshop : How ? (Strategy)
Must be connected with company VISION.
B- Learning to change
Explicitly reference (in VISION) the expected form of reasoning and learning to be attained from the change.
C- Ask powerful question to build VISION
- Determine sense of urgency
- Try to understand what inspires people
- Ask what would inspire you to change ?
- Verify expected goals
- Check what should be modified
- Determine what could be learned – once change done
- Identify current opportunities – once change done
- Determine product / personal risks are and required milestones
- Establish high level roadmap
D- Setting the transformation team
3/5 peoples every 100 (must be part of day-to-day work, not externals).
- Improving transparency & supporting the change
- Demonstrating behaviors
- Bringing to light dependencies
- Help unlearn old practices
- Creating necessary connections
- Ensuring necessary alterations are made
- … p.296
E- Importance of commitment in employees
- Treat as potential customers.
- Everyone should feel safe, learn everyday, and make collaborative decisions.
- 3 types of employees: committed,
non committed
Make people feel motivated during transformation
- Provide employees with the business context
- Help understand the constraints
- Use the real capacity
- Connect people with the client and the purpose
- Give time to discover and reflect
- Gamify the matter
- Dynamics
- Mechanics
- Components
- Create suitable metrics
F- Core values (Peter story)
- Company vision and strategy
Clear distribution of power- Behaviours / social systems
- Structures and their connections
- Control systems
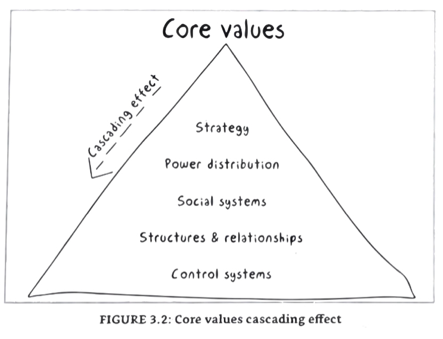
Down: more slow to transform.
- Convergence ≠ Transformation
- Convergence: reinforce current values.
- Re-creation: new values, new strategies… -> transformation
- Reduce complexity, improve communication…
G- Sustainable change in company
Start with a small team then expand.
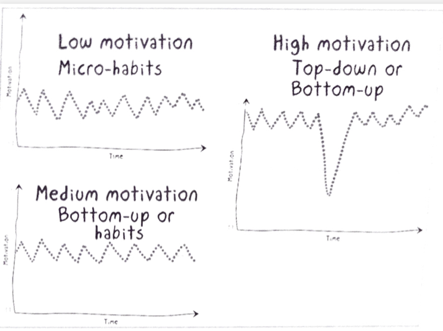
4 approaches to transform:
- Top-down
- Local to global (bottom-up)
- Little by little (organic)
- Micro-habits
- Top-down : employees can disagree
- Bottom-up:
pilot team should be highly motivated - Little by little: apply 1 principle at a time -> no urgency situation
- Micro habits: change little habits -> can have big impacts
- Habits (change in process)
4- Preparing your mind for the change
A- Confirmation bias
Confirmation bias is the human tendency to seek and use information that confirms preexisting opinion.
To overcome ask “How” questions or inverted questions.
People must understand that they need to change and feel comfortable with it. So they change habits.
Accelerate change
- Technical agility
- Structural agility
- Outcome agility
- Social agility
- Mental agility
- When the change become exponential people become motivated and push for the change.
- Change micro-habits.
- LINEAR thinking doesn’t work with exponential changes!
B- Neuroplasticity
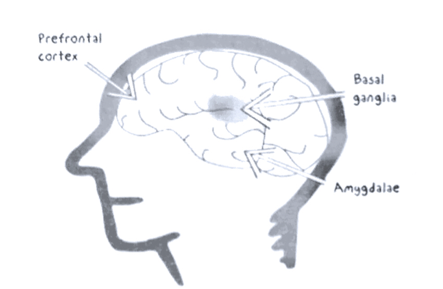
- Thoughts and actions are controlled by your emotions.
- During transformation, employees believe that the new plan put their role at risk:
- Your emotions make you decide before even analyzing the situation
- Logic only come if emotion allow it
- Your transformation strategy must have a clear purpose and be fun from the beginning
- Involve all the team: what’re the personal challenges you see in this plan or initiative?
- For every new activity prefrontal cortex (logic) has to make considerable efforts so you are more tired (amygdalae activates too)
- Once automated the activity is stored in the basal ganglia, consume little energy
- Amygdalae: smoke detector
- Can take control of the brain and sabotage your plan if too
much risks - It activates before even the emotion become conscious
- Must be kept deactivated
- Positive attitude decrease activation
- Negative thoughts must be spoken explicitly
- Possibility of change in rank is one of the most aggressive threats
Disproportionate reaction of amygdalae- Giving unsolicited advice is the second most aggressive
- Ask questions and make the person arrive
to the conclusion by himself - Perfection game
- Ask questions and make the person arrive
- Can take control of the brain and sabotage your plan if too
C- Micro-habits
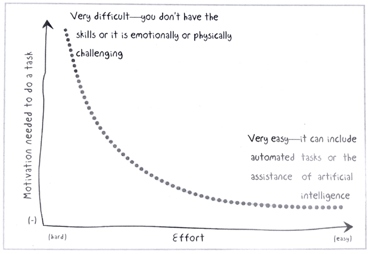
- Implement big changes when motivation is high, micro-habits changes can be successful even when motivation low.
- Increase motivation by involving the team in making decisions, use short cycles to measure, set small goals, let them choose their workloads, create a change vision… (p.149).
- Many habits are a huge set of micro-habits (automatic ≠ reasoned decisions).
- Identify the crucial moment that initiated the habit, be aware of benefits, change
and reward (ex: red sign bank).- Place, moment, emotional state, people involved, type of behavior, reward.
5- The 5 patterns to make change contagious
A- Motivated team
- Autonomy
- Mastery
- Purpose
B- 5 areas to make change contagious
Conflict resolution
- Runde and Flanagan resolution model
- Triangle drama: victim, persecutor, rescuer
- Be careful to not be part of the triangle
- TED: the empowerment dynamic
Reframing mindset
Rebooting the mind with a different operating system.
Change lens to see things.
Robinson Crusoe technique p.179
- Write 15 lines about the situation
- Add BUT at the end of each phrase
Perceptual position technique p.181
- Roles game
Exponential strategy
- The Team must be reminded why changes are done.
- The Team must know their rights, obligation, opportunities, roles: meeting to ask them opinions and expectations.
- Communities of practice
- Work on the following areas:
- Use real-time metrics
- Act as activists of a social movement
- Reaffirm why work is being done
- Use short work iterations: fast learning
- Use cloud technologies, AI, automation processes
- Use technologies, change organizational structures, prepare people for constant change
Expectations and alignment
Everyone should be at the same page, know the priorities, align on business value…
- Use a change backlog
- VSM: value stream map – www.lucidchart.com
PROCESS ALIGNMENT:
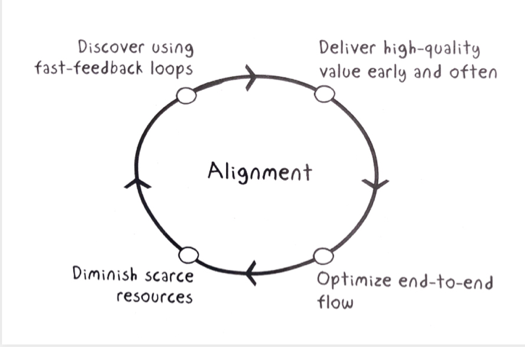
- Ensure you have a powerful vision and goals shared by the team
- Why are we doing this?
- Clear and share business value
- The Team must verbalize expectations
- Use SMART goals: specific, measurable, actions oriented, realistic, timely
- Involve people who can positively influence success
- Short work cycles, fast improvements
Psychological ownership
- Control on the product can give the feeling of ownership
- Knowing well the product can give the feeling of ownership
- Invest time in product give a feeling of ownership
- Rights and responsibilities
- Changes self-initiated
- Fairness, sense of community, active participation…
Ownership can be negative if we chose to left behind a product, important to learn how to get rid of a product for the team. The new product must be 2x more valuable. Create sessions to celebrate the change and compliment for the past.
Baader-Meinhof phenomenon: when you buy a mini you see it everywhere.
Before implementing the changes teach the patterns you think would have a positive impact, then they will start seeing them everywhere.
6- Preparing the transformation team
A- 3 stages for the change
- Feasibility, purpose and context of the initiative
- Let’s go ahead, not move forward or more info or short experiment need to be run first
- Budget should be based on the results of short work iterations, not for the entire initiative.
- Integrate customer in every step, transparency regarding obstacles and limitations
- Don’t invest in a project but in a value stream
- Clear process to refine the budget acknowledged by the team
- Prioritize work or experiments collaboratively
- Use budget to create better products
- Liftoff of the initiative
- Planning, estimation, prioritization and implementation
Short experiments and feedbacks (lean startup)
Transformation team must evaluate level of motivation, and suggest the appropriate strategies to use. Disappear once the change is done.
Hierarchy free, with different areas of expertise, passion, reframe, ability to work as a team, clear goals and comfortable working in pairs.
Measuring and evaluating scrum in
- Must be setup weeks before the start of the change plan
- Executive leader must be part or express support
- 3 to 5 persons 100% available every 100 persons
- External people, like coach, should focus on sharing knowledge with the team rather than taking charge of the change
- Self organized
- Use reciprocity
B- Once the transformation team is ready
Once The transformation team is ready,
Impact mapping: why? Who? How? What? p.223 (Team LIFTOFF) can be done also for a team reset when motivation
- Chairs in circle in the middle of the room
- Why are we doing this (change)?
- Who will be affected to achieve the goal?
- How should behaviors change?
- What experiment or simple task could be performed to confirm whether that minimum impact is viable?
C- Interactions map
D- Use values and working agreements
Use values and working agreements: values that need to be shared and respected by the team p.228
- Brainstorm meeting to define them
- For each meeting you plan, make clear the outcomes, participants,…
E- Change Vision Roadmap
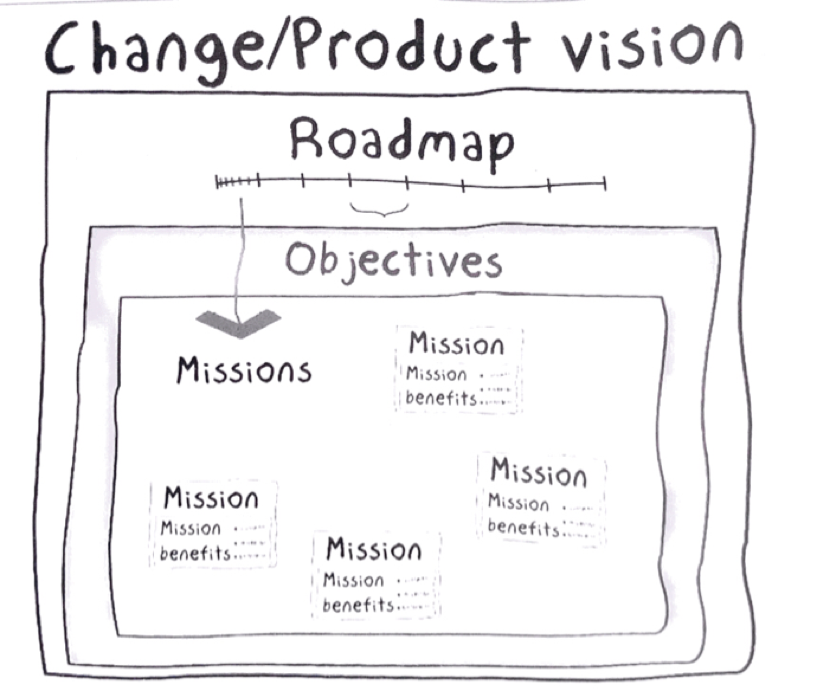
F- A5 canvas for each work cycle (3/5 days)
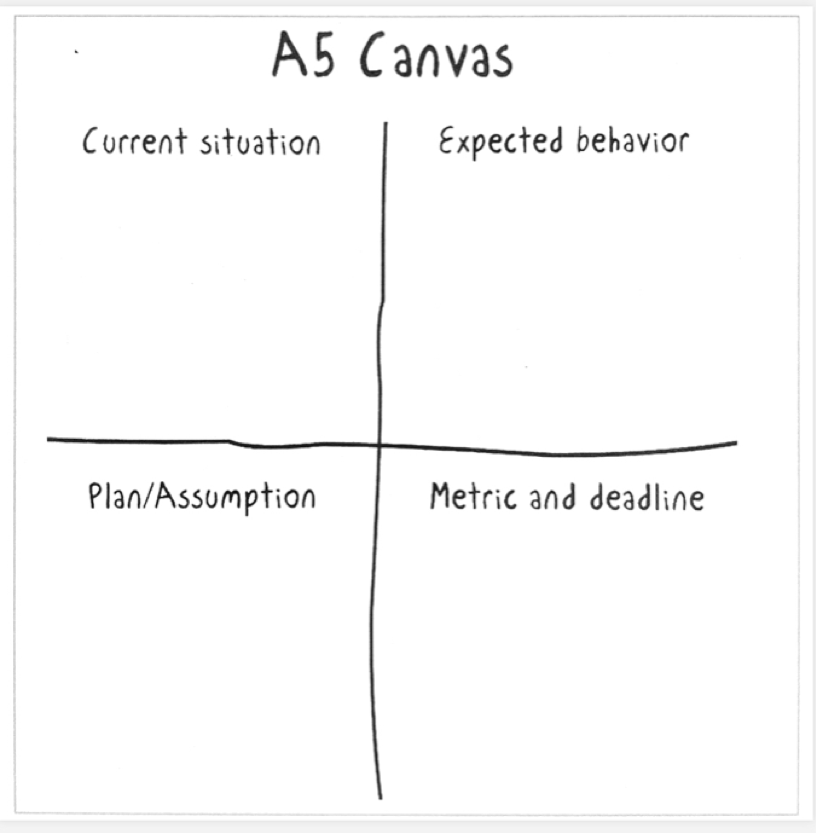
There must be a dedicated space: wall, window, tables…
G- Use Metrics
- Business performance metrics (KPI)
- Organizational health metrics
- Habit-improvement indicators (driver metrics)
7- Discover the power within your company with enterprise social systems
- Techniques should not be intrusive
- Any individual in the organization must be able to use the new guidelines
- Agile ≠ business agility
A- 4 layers of the organization
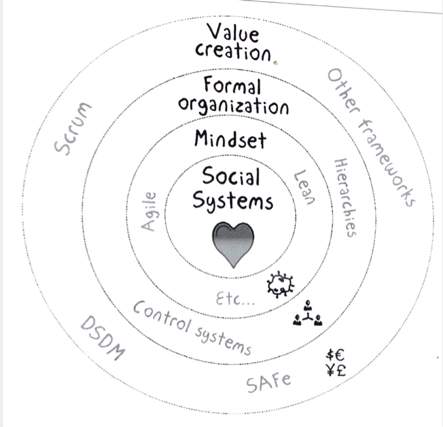
- Social systems
- Relationship between people
- Most impacting
- Mindset
- Beliefs and values
- Formal organization
- Structure that sustain work styles
- Value creation
- Frameworks
- Include the 4 layers to have a powerful plan
B- The 5 components (help in challenge time)
1- Enterprise blocking collaboration
Negative impact – Signs of existence: p.267
Work agreements to reduce it. Between members team and different teams.
2- Enterprise social density
- The more speed the information goes the better it is: informal faster than formal.
- Encourage informal, relevant communication in a safe environment.
- Make people work in pairs to share knowledge symmetric.
Direct form of communication.- Employees self-organized: no strong hierarchical structure.
CD3: cost of delay / duration prioritizing technique
GUIDELINES (p.275):
- Everyone in the value stream must be able to clearly identify the process, activities and individual involved.
- Face-to-face communication
- Direct access to other employees who could help them
- Bureaucracy actively simplified
- Individuals teach each other using communities of practice
- Safe to try
new ways of working - Informal structures that maximize relevant conversations
- People encouraged when the work to be done changes abruptly
- People encouraged to work in pairs
- Information provided by ai and big data available to everyone
3- Enterprise social visibility
- Work in the same space, not remotely
- Public information radiators: whiteboards, screens,…
- Everyone should see when updated
- Visible social interaction: shake hands
- Recognition of visible facial expressions
- Visualisation of actions and movements for recognition and prediction
- Connection between the value stream and the physical space
- Organize meetings, events with fixed cadence
sococo.com
Offices layouts: p.289
4- Complexity and complication pattern
- When something changes abruptly the brain tries to add steps, processes that give comfort
- Often counterproductive
- Complexity ≠ complication
- Things become more complicated, less capacity for innovation
- Keep complication levels low
- Starting a change initiative can complexifie more if already too much processes
DECREASING COMPLICATION:
- Use face to face as much as possible
- Try to not create new roles or departments, use cloud tools to simplify IT architecture
- If few employees often break company standard do not add new rules, look for creative solutions
- In any new plan managers should focus on removing obstacles instead of managing people
- Product with low quality increase complication
- Ensure people are not multitasking
- Have frontlines employees in contact with the client more flexible and able to make small adjustments to the process
- Build group consensus before meetings
- Before implementing a new framework be sure the team has a low level of complication
- People who work over 80% will increase level of complication
- Let teams to be self organized
- Have people in the company that are exclusively dedicated to removing obstacles
- Ensure individuals feel safe
- Do frequent reflection sessions to remove complication
- Reduce knowledge silos in teams
5- Permission to learn pattern
- Employees must be self organized, collaborative on what they want and how they want to learn
- Everyone should share his knowledge
- Workshop 100 people to form 8 scrum teams p.278
- 6 principles learning better
- Eliminate bureaucracy
- Communities of practice
- The teams should manage his own budget for learning
BONUS: Entreprise social Systems game
- Team of 6/7 people
- Several problems on sticky in center table
- Chose the most important
- Find a plan to solve it
- Then everyone take a role : expert density, expert visibility …
- Review the problem and change the plan according to each expert
8- Enterprise social systems: ELSA and DeLTA frameworks
A- Leader qualities
- Leads by example and inspires
- Makes time for others
- Generates empathy and is transparent with their thoughts
- Maintains focus during difficult times
- Inspires confidence with their actions, passion for their work
- Identifies logical connections between proposals
- Draws correct and well informed conclusions about necessary actions
- Distinguish what complex and what complicated
- Identifies relevant data and converts it into useful information
- Recognizes unproven assumptions, beliefs and values and challenges them when necessary
B- ELSA Framework
ELSA Framework:
- Requires a sponsor and leaders of the organization to support the initiative
- Event, Language, Structures, Agency
- Accelerate & Shortcuts
Priming
- Game: Danemark, elephant
- Importance of language
- Present tense more powerful than future tense
- Product requirement -> product hypothesis
- Backlog colour, green, yellow second week, red two last days
- Words about old people reduce speed in people who use them
- Location and context important: study: hot and iced cup of coffee
So imagine the perfect day with your 5 senses (EVENT) for the change and feel it
- What if the perfect day … ?
- Share via informal channels, encourage informal workspaces (STRUCTURES)
- Employees must have explicit permission and the right to fail (AGENCY)
- Associate employees with positive events
C- DELTA Framework
DELTA Framework is:
- D
ouble loop for transforming and accelerating - Contagious, no leader or sponsor needed
- Contagious by habits
8 habits to change (WHAT not HOW). Small improvement on each and move to the next.
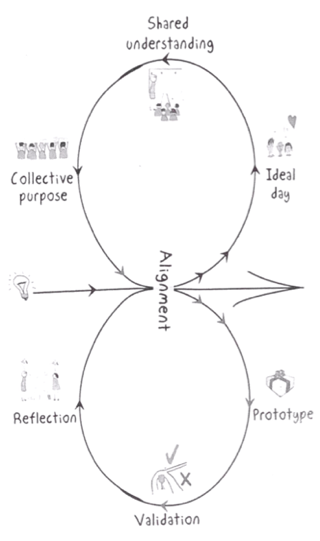
- Alignement: people should ask more questions about problem (meetings)
- Envisioning the ideal day (without the problem in question)
- Shared understanding: employees provide feedbacks to others
- Collective purpose: vision of change, working agreements…
- Alignement II: create conditions for the ideal day, easily make change in the organization
- Prototype: execute a plan without waiting for others
- Validation: compare what meant to be achieved vs what is finally achieved
- Reflection & improve on what can be done in general
